Downs , Edwards , Pataus |
Holt Oram syndrome hypoplastic thumb accessory phalanx, |
TAR syndrome |
Ellis van crevald syndrome |
Eisenmenger – cyanosis and clubbing |
Axenfeld rieger anomaly (AD- ocular anomalies) |
20-30 % more than 40 years have AF |
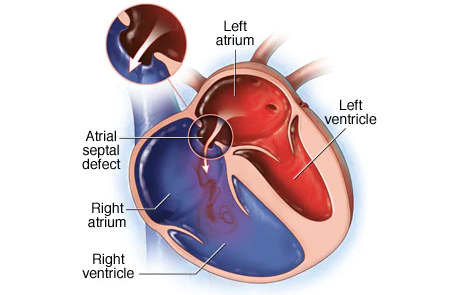
Normally a=v wave |
a>v wave small shunts , LV failure , PAH , LV dysfunction |
v>a wave large left to right shunts |
X descent well preserved |
Prominent left IJV > right s/o PAPVC into right atrium by LSVC/coronary sinus |
Normal apex in ASD is RV s/o increased amplitude and normal duration hyperdynamic and retraction during late systole |
Large shunts s/o sustained RV lift/heave even in absence of PAH(very large RV chamber displaying and occupying apex |
Palpable S3/S4 |
LV impulse minimal/absent |
RVOT/PA systolic thrill due to palpable PA |
RVOT pulsations |
Increased intensity of T1 , audible splitting S1 and delayed closure of T1 due to prolonged RV ejection |
Second heart sound wide and fixed splitting(except in infants and young children where its narrow as little or no shunt in either direction), Loud P2(dilated PA and brisk elastic recoil) |
Wideness due to prolonged RV ejection and increased hang out interval |
Fixed as RV filling remains constant in both phases of respiration |
Normal splitting in sinus venosus ASD |
Other d/d of WFS are RV dysfunction , Acute PTE and RBBB |
RVS3/RVS4 and Opening snap suggest Qp/Qs > 2:1 |
Pulmonary ejection sound in half of pts with ASD(soft and not as high frequency as PS) |
Pulmonary ejecrion murmur creasendo decrescendo after S1 and ends well before S2 |
If ASD murmur is grade 4-6- suspect associated pulmonary stenosis |
Other findings of associated PS in ASD– Longer and louder murmur , systolic thrill, loud click, P2 normal/prominent |
Diastolic murmur(TV flow murmur s/o Qp/Qs > 2:1 and starts in early diastole , increase on deep inspiration and leg elevation, hemodynamic significant left to right shunt |
Diastolic murmur across ASD - continuous murmur beginning in late systole and extends into diastole s/o lutembachers with restrictive ASD(associated MS) |
ASD with PAH and PR may have early diastolic murmur(grahams steel) |
Diatolic murmur of low pressure PR uncommon(aneurysmal dilatation of pulmonary trunk) |
Continuous murmurs through restrictive ASDs are rare |
Sinus node dysfunction as early as 2-3 years |
Accelerated atrial rhythm in 1/3 children with ASD |
AF , Atrial flutter and SVT by 4th decade |
Sinus arrhythmias does not occur |
Atrioventricular conduction defects(prolonged PR) |
Advanced first degree familial > non familial ASD |
Holt Oram first degree HB , sinus Brady and ectopic atria; rhythm |
Peaked right atrial P and prolonged P wave duration enlarged right atrium |
Normal p wave axis in OS ASD compared to SV ASD where it is inverted in inferior leads and upright in AvL( ectopic atrial rhythm);QRS axis vertical and clockwise depolarization q in inferior leads |
RBBB; rad(symptomatic PAH or pulmonary vascular ds);LAD exceptional represents LAHB in older pts |
Crochetage sign(OS and SV ASD) sometimes shunt severity; also seen in PFA |
Increased vascularity to peripheral lung fields |
Pulmonary trunk and proximal branches dilated |
Asc aorta is seldom border forming |
Jug handle appearance |
SV ASD accompanied by localized ampullary dilatation of SVC proximal to attachment of RA |
Aneursymal dilatation of MPA in extreme PAH |
RA enlargement; LA enlargement in pts with AF and older pts |
RV enlargement |
© 2022 Cardio Blogger. All Right Reserved | Designed & Developed By Diviants